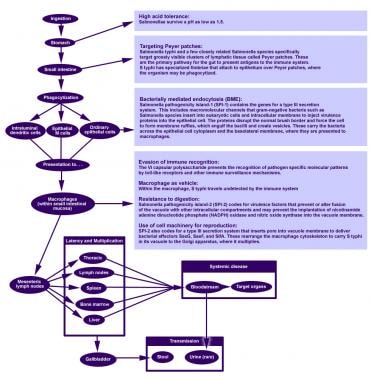
Pain in the upper right part of the abdomen. Cases in patients under the age of 36 months should be classified using the Perinatal HCV Position Statement except when the exposure is nonperinatal.
Acute hepatitis C is most often diagnosed in the setting of post-exposure surveillance or seroconversion in high-risk individuals eg health-care professionals or injecting drug users previously known to be seronegative.
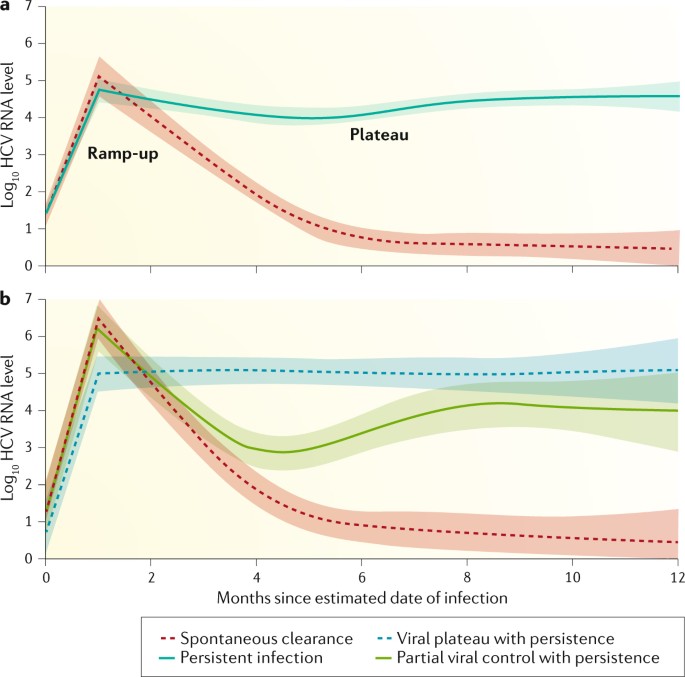
Acute hep c. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. People should be considered for treatment if their infection becomes chronic. Acute hepatitis is a general diagnosis referring to any of a wide variety of conditions causing acute inflammation or injury to hepatocytes resulting in elevation of liver biochemical lab tests.
Although transmission via transfusion and injecting drug. Symptomatic acute hepatitis C occurs in only about 15 of patients who are infected with hepatitis C virus HCV. Patients with acute hepatitis C are often asymptomatic or have nonspecific symptoms eg fatigue anorexia mild or moderate abdominal pain low-grade fever nausea andor vomiting that frequently are not recognized as being associated with acute HCV infection.
In the small number of people who get sick during the acute infection signs and symptoms include. Acute hepatitis C develops two weeks to six months after the hepatitis C virus enters your bloodstream. It is a type of viral hepatitis.
Yellowing of the skin jaundice Dark urine. This implies that the majority of initial HCV infections in children are asymptomatic. A different virus is responsible for each type of virally transmitted hepatitis.
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus HCV spread through contact with infected blood. Symptoms range from none to very severe. Acute hepatic injury is confirmed by a raised serum alanine transaminase activity.
There is not a recommended treatment for acute hepatitis C. Current treatments usually involve 8-12 weeks of oral therapy pills and cure over 90 of people with few side effects. There are several medications available to treat chronic hepatitis C.
Alkaline phosphatase and γ-glutamyltransferase activities can also be raised in patients with an acute hepatic injury but their activites are usually proportionately lower than that of alanine transaminase. After initial infection the virus clears spontaneously in an estimated 20 to 35 of patients. Info for the public and health professionals.
In most people the inflammation begins suddenly and lasts only a few weeks. Acute hepatitis due to HCV appears to be an uncommon presentation in childhood. Learn about hepatitis C transmission prevention vaccination and symptoms.
When it presents acutely it cannot be distinguished on clinical grounds from other forms of viral hepatitis. Acute hepatitis C HCV infection is defined as the 6-month time period following exposure to the hepatitis C virus. The activity may be 100 times normal and no other biochemical test has been shown to be a better indicator.
Hepatitis A is always an acute short-term disease while hepatitis B C and D are most likely to become ongoing. The incubation period is 4 to 8 weeks. Occasionally a fever dark urine abdominal pain and yellow tinged skin occurs.
Acute viral hepatitis is inflammation of the liver caused by infection with one of the five hepatitis viruses. A small proportion. Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus HCV that primarily affects the liver.
These patients never develop chronic hepatitis C infection. A new acute case is an incident acute hepatitis C case in a person older than 36 months of age that meets the case criteria for acute hepatitis C and has not previously been reported.