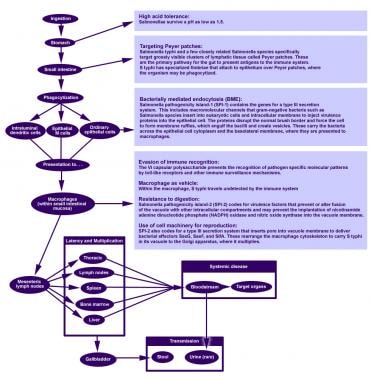
Postoperative urinary retention urinary bladder surgical procedures operative urinary catheterization BLADDER catheterization is a common procedure during inpatient major surgery that allows monitoring of urine output guides volume resuscitation and serves as a surrogate marker of hemodynamic stability. Please go to the nearest emergency room or call an ambulance if you require immediate support.
 What Is A Foley Catheter Uses Types Products Hcd
What Is A Foley Catheter Uses Types Products Hcd
Otherwise admit the man urgently for catheterization and investigation of the cause.
Urinary retention catheter. Acute urinary retention is an immediate life-threatening urologic emergency that is often treated with a catheter. Acute urinary retention is a medical emergency and your doctor will quickly place a catheter into your bladder to let out the urine. Catheters may be used as a long-term solution where persistent urinary retention is causing incontinence infection or renal dysfunction and a surgical solution is not feasible.
Accepted indications for urinary catheterization are listed in Table 1. In some cases people with urinary retention need to continue using a catheter to drain urine from the bladder until their urinary retention can be fixed. 4 7 An initial episode of acute urinary retention should be treated with an indwelling catheter to allow the bladder to.
A catheter is not always needed straightaway if you have persistent chronic urinary retention. Their use is associated with an increased risk of adverse events including recurrent urinary infections trauma to. Chronic urinary retention is a long-term medical condition with.
Urinary catheters come in. See your doctor right away or go to the Emergency Department if you cannot urinate at all or you are in pain in your lower tummy or urinary tract area. Discuss and decide on treatment to prevent or manage recurrent urine retention.
Urinary retention that cannot be monitored or addressed by bladder scannerintermittent straight catheter ISC eg. If the man has recurrent acute retention or acute-on-chronic urinary retention admit the man or insert a urethral catheter. People with chronic urinary retention typically require intermittent catheterization.
This is the quickest and easiest procedure. However if the cause of your chronic urinary retention cannot be treated or the urinary retention is causing damage to your bladder or kidneys you may need a long-term catheter. Acute urinary retention needs urgent medical attention and your bladder may need to be emptied using a urinary catheter which is a long soft tube.
Spinal cord injury Anticipated urinary retention due to paralytic medications Recent urologic or gynecologic diagnosis or procedure for which catheter removal is not yet recommended. A catheter needs to be used as soon as possible if you have sudden acute urinary retention. In terms of medical social and economic resources the burden of urinary retention and incontinence aggravated by the use of the Foley catheter is huge.
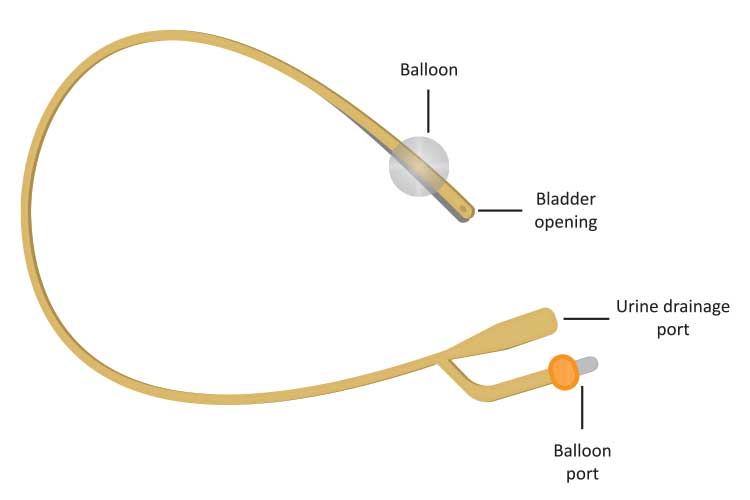
A urinary catheter is a hollow partially flexible tube that collects urine from the bladder and leads to a drainage bag. The catheter can be indwellingleft in your bladder for a short or long time or intermittentinserted to drain the bladder when needed and then removed. Urinary retention being unable to empty your bladder when you need to Surgery on the prostate or genitals Other medical conditions such as multiple sclerosis spinal cord injury or dementia Catheters come in many sizes materials latex silicone Teflon and types straight or coude tip.
This review evaluates the effectiveness safety patient preference cost-effectiveness and budget impact of different types of intermittent catheter IC. In the UK the harm resulting from the use of the Foley catheter costs the National Health Service between 10.