The alpha-gal allergy was only identified in 2006 and doctors are still learning about the condition. Is sensitized to alpha-gal.
The three dominant forms of mammalian meat allergy are Alpha-gal syndrome.
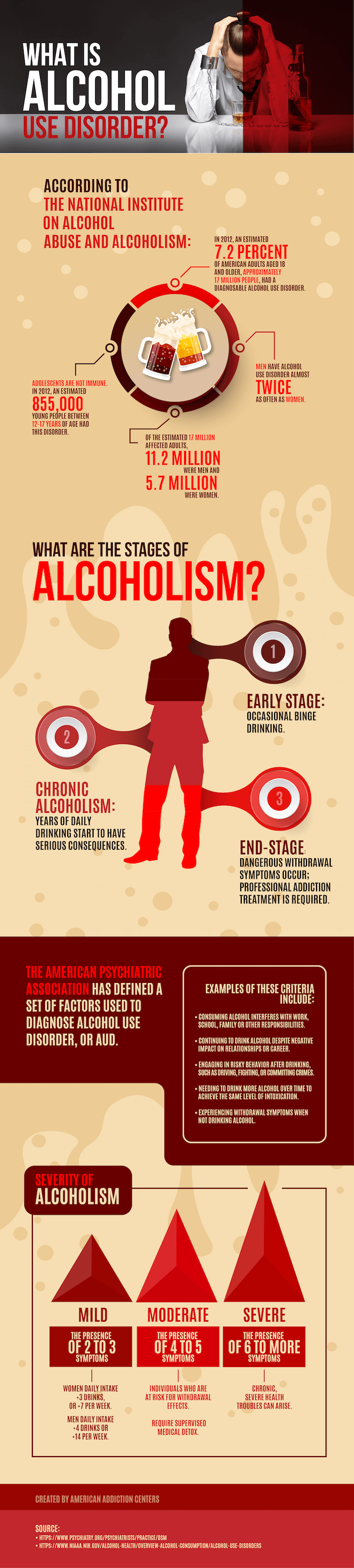
How common is alpha gal allergy. These allergies differ from each other in significant ways. Cases of alpha-gal allergy are becoming increasingly common but are still considered rare. Today than it was a decade ago with the number of laboratory-confirmed cases growing from 12 in 2009 to over 34000 in 2019.
Alpha-gal syndrome is a recently identified type of food allergy to red meat. Scott Commins describes alpha-gal allergy which scientists believe is triggered by a tick bite and can cause a reaction to red meat. Researchers now believe that some people who have frequent unexplained anaphylactic reactions and who test negative for other food allergies may be affected by alpha-gal syndrome.
Orlando FL - Red meat allergy is a recently recognized allergic reaction to the substance galactose-α-1 3-galactose alpha-gal. New research suggests that some blood types may have a protective effect against the allergy. And other populations with high tick exposure including areas of the Midwest and much of the eastern US.
Of the population in the southern US. It triggers an immune system reaction that later produces mild to severe allergic reactions when they eat red meat. Most of the southeastern US.
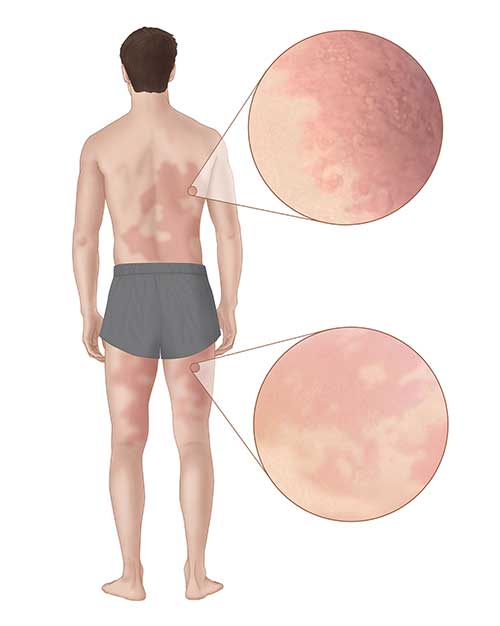
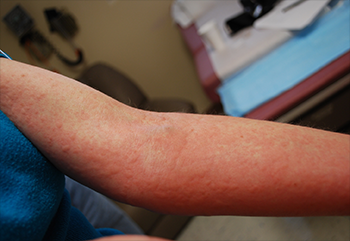
Commins talks about the symptoms of a reaction how one can be tested for the allergy and changes in diet recommended for patients who have alpha-gal. The symptoms of meat allergies are similar to those of other kinds of allergiesHives headaches and a runny nose after eating meat from a mammal are all common with alpha-gal allergy. And large areas of the Midwest and eastern US.
The most common venom sensitization among alpha-gal allergic patients was to common wasp to which 303 of patients were found to be sensitized. Patients with alpha-gal allergy reported a higher rate of allergic reactions following insect stings and were five times more likely to be sensitized to honey bee white-faced hornet common wasp paper wasp or fire ant than patients without the allergy. Alpha-gal is short for Galactose-alpha-13-galactose a carbohydrate molecule found in mammalian meats of which beef lamb and pork are the most common in the American diet.
Alpha-gal syndrome AGS also called alpha-gal allergy red meat allergy or tick bite meat allergy is a serious potentially life-threatening allergic reaction. Unlike common food allergens which are usually proteins this allergen is a carbohydrate sugar. In susceptible individuals multiple tick bites can result in sensitization to the allergen galactose-alpha-1-3 galactose alpha-gal which is present in many non-primate mammalian tissues.
Alpha-gal is a sugar found in red meats including beef pork venison and lamb and for a small percentage of adults and children who have been bitten by a tick who have transferred alpha-gal to them it can develop allergic reactions after eating these meats. There is more than one mammalian meat allergy. Scott Commins is an Associate Professor of Medicine in the Division of Rheumatology Allergy and.
Alpha-gal syndrome is commonly contracted from being bitten by a tick most typically the lone star tick. AGS may occur after people eat red meat or are exposed to other products containing alpha-gal. Alpha-gal syndrome is a much more common allergy in the US.
An allergy to the sugar galactose-alpha-13-galactose alpha-gal in mammalian meat other parts of mammals and products derived from them Primary beef allergy. Unfortunately AGS has no insurance billing code ICD code nor is it a reportable illness to the CDC. Id recently read a random article on alpha-gal syndrome AGS a food allergy to red meats and products made from mammals that most often begins when youre bitten by a Lone Star tick.
The a-Gal syndrome is a regionally common form of food allergy that has a characteristic but not universal delay in symptom onset includes gastrointestinal symptoms can develop at any time in life and is equally common in otherwise nonatopic individuals.