Ductal hyperplasia can be seen in both breast and cervical cancer--the 2 most common female cancers that afflict women. Papillomatosis often used interchangeably with ductal hyperplasia is a term more appropriately applied to hyperplastic lesions in which a distinct fibrovascular structure supports papillary epithelial hyperplasia.
 Atypical Hyperplasia Dr Susan Love Foundation For Breast Cancer Research
Atypical Hyperplasia Dr Susan Love Foundation For Breast Cancer Research
Usual hyperplasia poses no risk and is not a problem of any sort.
Is atypical ductal hyperplasia hereditary. After a diagnosis of ADH on biopsy a proportion are upgraded to carcinoma upon excision. These cells share some but not all of the features of low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ DCIS both in terms of growth patterns and appearance. Written by Becky Young Updated on September 18 2018 Cancer risk.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia ADH and atypical lobular hyperplasia ALH. Screening breast MRI demonstrated a suspicious mass and MRI-guided biopsy revealed atypical ductal hyperplasia. Atypical lobular hyperplasia ALH increases your risk of developing breast cancer in both breasts.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia ADH Atypical lobular hyperplasia ALH Breast cancer risk is about 4 to 5 times higher than normal in women with these changes. Ductal hyperplasia that is not atypical is referred to as usual regular or. When the cells grow to look funny then the collection is described as atypical hyperplasia.
Breast cancer is thought to develop from noninvasive precursor lesions although the earliest steps of neoplastic transformation are still undefined. Atypical ductal hyperplasia ADH In ADH the new cells that grow look like the cells that grow in your breast ducts. However the remainder of patients are overtreated.
Usual ductal hyperplasia UDH is considered to represent a benign proliferation of ductal epithelial cells whereas atypical ductal hyperplasia ADH may represent the first clonal neoplastic expansion of these cells. Analysis of loss of heterozygosity in 399 premalignant breast lesions at 15 genetic loci. While ADH is considered a non-obligate precursor of invasive carcinoma the molecular.
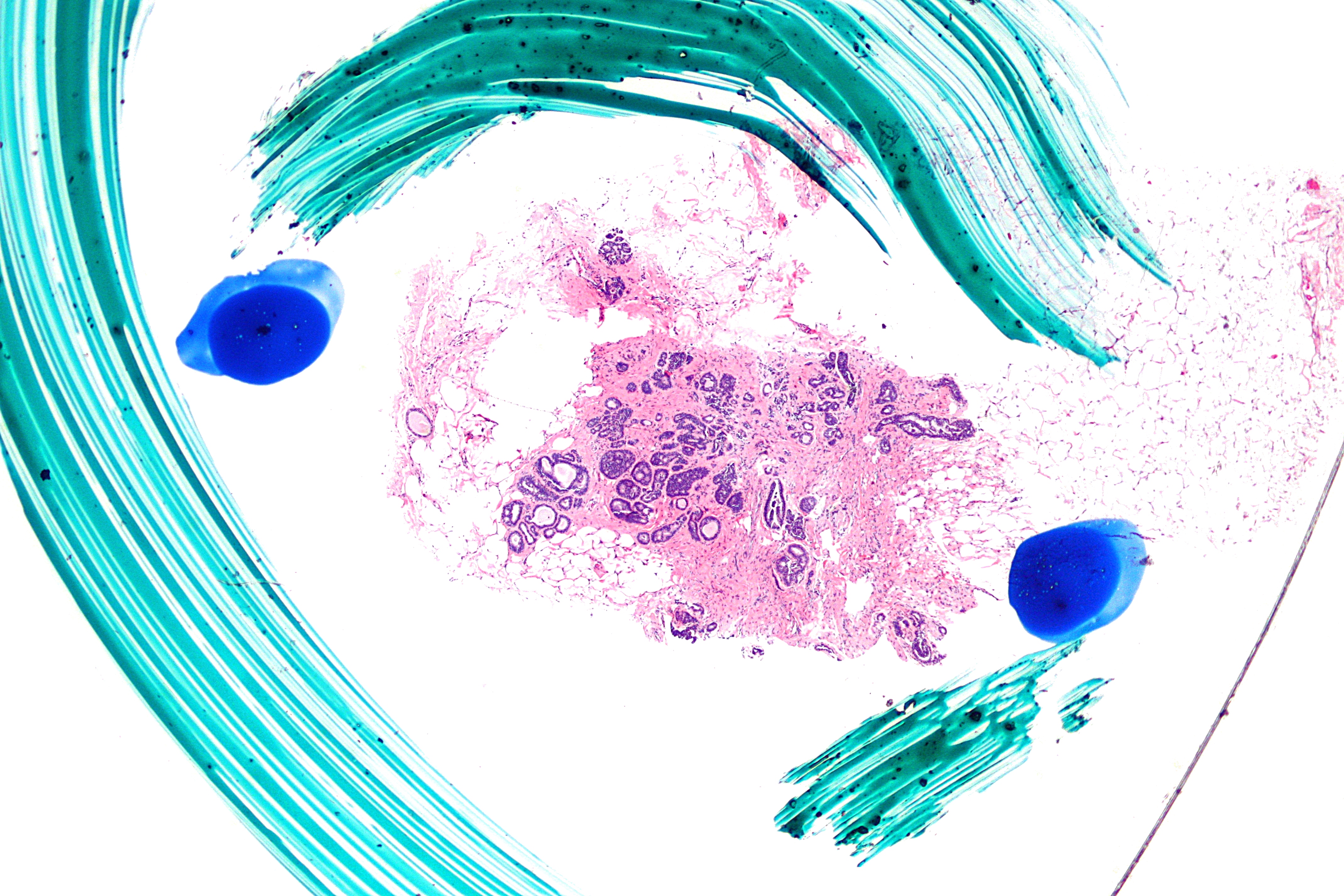
Atypical ductal hyperplasia ADH increases your risk of breast cancer occurring in the breast where the ADH was found. Women who carry mutations in BRCA1 BRCA2 PALB2 or CHEK2 will meet this risk threshold. Pictured above is the microscopic view of what these cells look like.
Endometrial biopsy EMB was negative for neoplasia. While ADH isnt cancer it may increase your risk of getting breast cancer in the future. If a woman also has a family history of breast cancer and either hyperplasia or atypical hyperplasia she has an even higher risk of breast cancer.
Hyperplasia means fast or quickly growing and atypical because the cells have begun to lose the clear borders of their cell membranes. Between an atypical proliferative lesion and an intraductal or invasive ductal carcinoma. There are 2 main types of atypical hyperplasia.
ADH is a benign breast condition linked to a moderate increase in breast. Atypical ductal hyperplasia ADH is a common diagnosis in the mammographic era and a significant clinical problem with wide variation in diagnosis and treatment. Depending on the location of this collection this collection of abnormal cells can be called by numerous different names.
Genetic testing for PTEN mutations identified a deleterious PTEN mutation N48K. Atypia and hyperplasia are thought to be reversible although it isnt clear what can nudge them back to normal. Understanding Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia Medically reviewed by Yamini Ranchod PhD MS.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia ADH. The patient underwent a coordinated risk-reducing total abdominal hysterectomy bilateral salpingo. Other women with family history of breast cancer or a history of a breast biopsy showing high risk changes such as atypical hyperplasia may meet this criterion as well.
With atypical ductal hyperplasia ADH there are more cells than usual in the lining of the breast duct the tube that carries milk from the lobules milk sacs to the nipple.